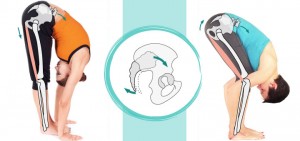
Three types of digestive discomfort and what we can do about them in yoga
0When you plan to use your yoga practice to aid digestion, images of deep twists might begin to crowd your mind. We’ve been conditioned to believe that twists are great for moving things along. This might be true in some cases, and ill-advised in others.
When we encounter digestive issues, the first thing we do in yoga therapy is identify the symptoms and then try to deduce what kind of qualities and direction of movement they represent. Based on that assessment, we chart a course of action to deal with the discomfort. Let’s take a look at three most common scenarios.

If somebody experiences an abdominal discomfort that’s accompanied by constipation, cramps and bloating, in yogic interpretation this would mean that waste is having trouble moving downwards. It also points to a hypo condition, when there is not enough activity in certain parts of the digestive tract. In a situation like that, we would try to gently stimulate peristalsis (intestinal contractions), increase heat in the system (to fan the flames of agni, digestive fire) and generally use stronger movements with intentional abdominal contraction. Deeper twists might be appropriate here.
If somebody experiences a belly ache that is accompanied by diarrhea, agitation and nervousness, we would say that the body is having trouble holding on to things. It also points to a hyper condition, when there is too much activity both in the digestive tract and the nervous system. In that situation, we would focus on soothing the system, activating the parasympathetic response and generally choosing more gentle movements and breathing practices. Some simple twists might still be effective, but our emphasis would be on releasing tension within the abdomen, rather than compressing it.
If somebody experiences irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) that is manifesting as abdominal pain, gas, diarrhea or constipation, we would view it as an irritation and/or increased sensitivity within the system. We would try to calm the system down and reduce and/or eliminate the stress factors that contribute to its reactivity. Sometimes referred to as “spastic colon”, IBS is often linked to irregular contractions of the large intestine. If irregularity (in flare ups and bowel movements) is an issue, we would seek to introduce rhythm and consistency with our asana and breathing practice.
As you can see, here we are less concerned with specific poses and movements and more with a particular effect they have on the system. There are several different spectrums that we would consider and ask ourselves the following questions: Do the symptoms indicate that the digestive system is overactive (hyper) or underactive (hypo)? Is there too much heat or too much coolness in the system? Is it stagnant or highly irregular? In general, we try to figure out where on each spectrum the symptoms land, and then supplement the system with whatever it is missing in order to move it closer to the state of balance. That way we end up working with chemistry and energetics, rather than just general abdominal compression.
Starting next week, we will feature several different practices that illustrate the examples described above as part of our Zoom In Within series. If you would like to follow along, please sign up for a HappyU newsletter or subscribe to my YouTube channel.

And before we dive in, it might be useful to refresh your memory on how different organs of your digestive system work >
Hope that you will join in!
Subscribe to HappyU newsletter >