Predictions: How your yoga students’ brains respond to your class instructions
2Any yoga teacher knows that it feels very different to teach regular students that have been coming to your classes for some time and brand-new students, especially the ones that are used to practicing in a different tradition. The regular students will sail smoothly from pose to pose, while students who are not familiar with your teaching style, your common cues, your class structure and so on, will have to concentrate harder, look around them more often and get confused more easily. This is perfectly normal and is a simple example of your brain’s reliance on predictions.
When a student is completely new to yoga, her brain forms predictions about yoga based on what she had seen on TV and in magazines, what she heard from people around her, and her own experience with other types of movement. Once she begins her yoga class those predictions might match her incoming sensory input, or not.
“Through prediction and correction, your brain continually creates and revises your mental model of the world. It’s a huge, ongoing simulation that constructs everything you perceive while determining how you act. But predictions aren’t always correct, when compared to actual sensory input, and the brain must make adjustments.” (1)
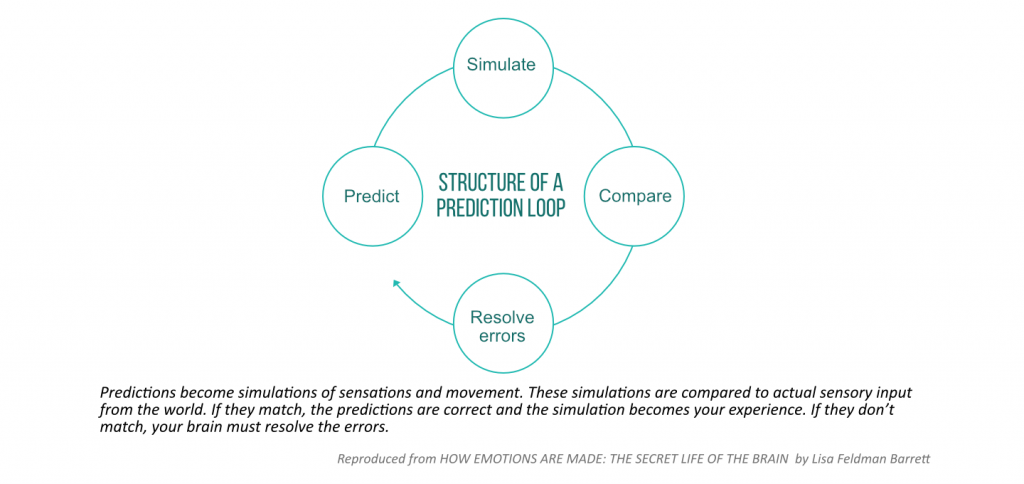 Any conflict between the brain’s prediction and incoming input needs to be resolved. So the new student will probably adjust her predictions based on the incoming input (your instructions) and it will become part of her experience. She will gradually learn how you expect her to position her body, how to breathe, where to direct her mind and so on. Adjusting our predictions based on incoming sensory input is an essential part of any learning process. Over time she will be able to predict more easily what you expect from her in your yoga classes and her predictions and her sensory input will become more aligned.
Any conflict between the brain’s prediction and incoming input needs to be resolved. So the new student will probably adjust her predictions based on the incoming input (your instructions) and it will become part of her experience. She will gradually learn how you expect her to position her body, how to breathe, where to direct her mind and so on. Adjusting our predictions based on incoming sensory input is an essential part of any learning process. Over time she will be able to predict more easily what you expect from her in your yoga classes and her predictions and her sensory input will become more aligned.
When the student is coming to your class from a different yoga tradition and has learned to do things a certain way, she will also encounter prediction conflicts in a new-to-her yoga class. Her brain will also need to resolve those conflicts. For example, if the student is used to looking up in Warrior 1, she will automatically do that. If you ask her to look forward instead, her brain has two options: to adjust her predictions about the pose and follow the sensory input (your request), or to ignore her sensory input completely.
When you have to repeat the same instructions several times and students keep ignoring it, most times this happens not because of ill will on the part of the student, but because they simply do not hear you, as their brains are choosing to use its own predictions to override the sensory input. In those situations it is helpful to rephrase your request and say the same thing few times with different words in hopes of getting through the prediction errors.
In other instances, the student might consciously choose to do the pose the way she was previously taught because she thinks that this is the correct way of doing it. Even if she begrudgingly follows your advice and does what you ask, she is likely to have a more negative reaction to your class in general. This happens because throughout the class her predictions are constantly being challenged, which is more jarring for the brain and demands more mental energy. It might help if you articulate your reasons for doing things your way and emphasize that you are asking her to do it for a specific purpose (like lengthening the back of the neck, or preparing for the next pose), rather than undermining everything she had learned and has been relying on in terms of yoga. Offer it as an option and invite all your students to experience it; this might encourage them to adjust their predictions and continue on through the learning loop.
In the viniyoga tradition we also challenge the brain’s predictions on purpose, to encourage focus and concentration. Next week we will discuss some of the techniques we can use to do that – check it out!
 References
References
- How Emotions Are Made: The Secret Life of the Brain by Lisa Feldman Barrett

















This is a great article which explains neurologically what I have noticed for many years…that some of my students seem NOT TO HEAR me … and then others hear me and change what DOESN’T need changing. haha. I really appreciate the (second to the) last line of the article, that this style helps encourage focus and concentration…I AGREE! My husband asked me why don’t I just name a pose and let people get into it and I explained that my intention was more to allow the student to experience the small movements that take us INTO a pose, to learn to pay attention to what’s going on inside so that they can carry that with them throughout their day.
I absolutely agree with Cherie’s comments, and am, once again, very grateful for your insights, Olga! Yoga instructors who teach with an awareness of why they are doing what they are doing (the poses and the transitions) and with an in-class awareness of what and how their students are doing (as I would like to believe I do!), can really benefit from these insights, Olga. Additionally, when I am the student, wow, do I know these thoughts/ideas that you just described. What a wonderful article, Olga! Thank you!