What could possibly be going on with your neck? Three main reasons for neck tension
2What do you do when you are startled, or if you hear, see, smell or sense something unusual? You immediately turn your heard toward it to see what’s going on. This is a natural survival instinct that is essential in the animal world for both the predator (to follow the prey) and the prey (to keep track of the predator). Quick and precise movements of the head were always essential to our survival as species. May be that’s why the two major muscles of the neck and upper back (trapezius and sternocleidomastoid) are innervated by the cranial nerve XI (also called “spinal accessory nerve”), unlike all other muscles of the body, which are innervated by the spinal nerves.
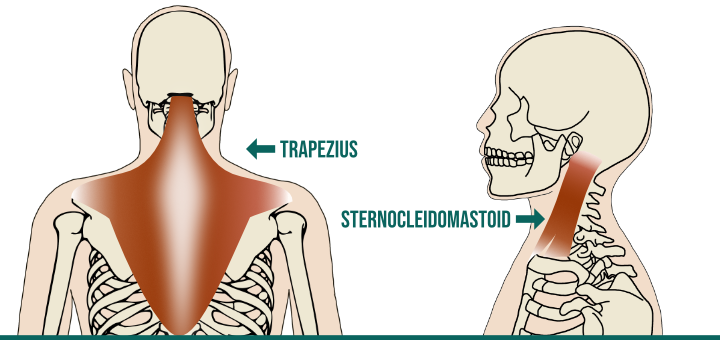
Why does it matter? It matters because cranial nerve XI is intertwined with the famous Vagus nerve that regulates the state of our autonomic nervous system. This tells us that the tone and activity of the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscles are closely tied to the state of our autonomic nervous system.
Both of those muscles have an interesting story in human development.

Stage 1: The first major muscular movement that a new human masters, is being able to lift the head up (by using her upper trapezius muscles) and then turn her head to look around (by using her SCM muscles) and take in the world through her senses.
Stage 2: The baby learns to prop herself up with her arms and lift the upper body up slightly. The baby arches her lower back (action of the lower trapezius), pulls the shoulders together (action of the middle trapezius), and tips the head back (action of the upper trapezius). She turns the head from this position by engaging her SCM.
Stage 3: The baby transitions up on all fours and begins to crawl, which requires her to use her trapezius muscles asymmetrically to move the arms while supporting the weight of the upper body on her hands. “When we first came up to crawl on all fours, the trapezius muscle held our head up high. The three parts of the trapezius functioned like a single muscle in which all of the fibers had roughly the same tension. Some of the muscle fibers worked to pull the shoulders back and together to support our upper spine, and other fibers pulling in other directions worked to lift the head back and up.” (1)
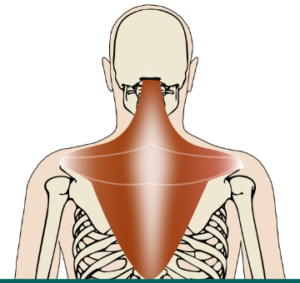 Stage 4: Once the baby transitions up into standing, the whole structural arrangement is completely changed – now those same muscles are responsible for holding the head upright and turning it in various direction from that new position. Since it is no longer required to support the weight of the upper body on her hands, the function of trapezius muscles is modified. “Rather than acting as a single muscle, these muscle fibers organized themselves into three functional units—now seen as the upper, middle, and lower trapezius—and these three groups of fibers began to work as separate entities. One part, therefore, might be overly tense while another part is under-tensed.” (1)
Stage 4: Once the baby transitions up into standing, the whole structural arrangement is completely changed – now those same muscles are responsible for holding the head upright and turning it in various direction from that new position. Since it is no longer required to support the weight of the upper body on her hands, the function of trapezius muscles is modified. “Rather than acting as a single muscle, these muscle fibers organized themselves into three functional units—now seen as the upper, middle, and lower trapezius—and these three groups of fibers began to work as separate entities. One part, therefore, might be overly tense while another part is under-tensed.” (1)
As the kid gets older, she continues to occasionally crawl on all fours, or climb trees, or throw a ball, or wrestle with friends, or do monkey bars – all those activities maintain good tone in her neck and upper back muscles. But as we get older and choose different occupations and lifestyles, we begin to develop other kinds of movement patterns that can make our neck and upper back muscles tense, flaccid or imbalanced, which causes neck tension, upper back stiffness, poor posture, headaches, and all sorts of other problems.
There are three main reasons why we get neck tension: overuse, underuse and abuse.
Reason 1: Overuse
 A friend of mine is a violinist for the Detroit Symphony Orchestra, which means that she spends many hours every day leaning and turning her head to one side, while holding her arms up, to play her violin. Eventually she had developed severe pain in her neck and upper back and couldn’t work. Since her livelihood depends on her ability to play her instrument, she was extremely stressed out when it happened, which probably didn’t help with her neck tension, since our neck muscles respond quickly to the state of our autonomic nervous system. There are many other occupations that are at risk of developing serious problems from overusing the muscles of neck and upper back, including construction workers and electricians who have to look up, hairstylists who have to hold their arms raised, airport workers who move heavy luggage, teachers who frequently turn their heads, and many others. If you have an occupation that requires repetitive motion of your neck and upper back, it is essential to have a regular movement routine that helps release tension in the muscles that are most affected and to calm your nervous sateen down. It is also very important to analyze your habitual movement patterns and get a very clear idea of which part of the neck is tense (see practice below).
A friend of mine is a violinist for the Detroit Symphony Orchestra, which means that she spends many hours every day leaning and turning her head to one side, while holding her arms up, to play her violin. Eventually she had developed severe pain in her neck and upper back and couldn’t work. Since her livelihood depends on her ability to play her instrument, she was extremely stressed out when it happened, which probably didn’t help with her neck tension, since our neck muscles respond quickly to the state of our autonomic nervous system. There are many other occupations that are at risk of developing serious problems from overusing the muscles of neck and upper back, including construction workers and electricians who have to look up, hairstylists who have to hold their arms raised, airport workers who move heavy luggage, teachers who frequently turn their heads, and many others. If you have an occupation that requires repetitive motion of your neck and upper back, it is essential to have a regular movement routine that helps release tension in the muscles that are most affected and to calm your nervous sateen down. It is also very important to analyze your habitual movement patterns and get a very clear idea of which part of the neck is tense (see practice below).
Reason 2: Underuse
If you don’t use your neck and upper back much during the day, your muscles will lose their tone. If you rarely look up or to the side (turning your whole body instead), if you don’t raise your arms much, if you never support your weight on your hands, if you never bend back – in short, if you keep the movement of your upper body and head very limited, your muscles will become flaccid and weak.
Reason 3: Abuse

If you spend long stretches of time in front of the computer or electronic devices, your head is likely to move forward in relation to your upper body, which pulls strongly on the muscles of the neck and upper back and causes tension there. The state of your autonomic nervous system might also show up in your posture and your muscle tone. If you are feeling agitated during your work day, you might assume a defensive posture that protects your heart, but at the same time stay alert and hyper vigilant by holding your head forward and up, expecting danger to come from any direction. If you are feeling withdrawn and resigned, like you cannot fight any longer, you might draw your head into your shoulders, assume a collapsed posture, and experience a general sense of weakness.
Where do you stand? Do you overuse, underuse or abuse your neck and upper back? How do you hold your head? Where exactly do you feel neck tension? To get a better idea about what’s going on, try this short Assessment Yoga Practice for Neck and Upper Back and record your findings on the included Observation Sheet.
Next week we will discuss what you can do to deal with different kinds of neck tension – tune in!
Observation Sheet for Assessment Yoga Practice for Neck and Upper Back >
Sequence Wiz members can add this sheet to their accounts and modify it any way they like. Learn more about Sequence Wiz membership >
[jetpack_subscription_form]
References
- Accessing the Healing Power of the Vagus Nerve: Self-Help Exercises for Anxiety, Depression, Trauma, and Autism by Stanley Rosenberg
















Oh my God Olga, you are the best teacher in the world!!!! Your explanations are so clear!!!
This is so timely for me. Thank you. I very much appreciate it. Milena