The art of observation in yoga: Reading the student’s body story
2Our bodies reflect our personal stories and our journeys, both physical and psychological. They hold traces of our daily movement patterns, history of injuries (physical and emotional), and hints of internal imbalances. If we want to be helpful to our yoga students, we need to learn to read the messages that the body displays and to help our students make sense of their own body stories.
As yoga teachers and yoga therapists, we are continuously working on perfecting our observation skills to be able to understand our students on a deeper level. We conduct those observations in stillness and in motion, because different layers of the systems are revealed in different positions and at different times. We observe our students as they sit, stand and lay on the ground, as they move through yoga poses and hold them. Little by little we collect pieces of information about the student’s body and their relationship with it.
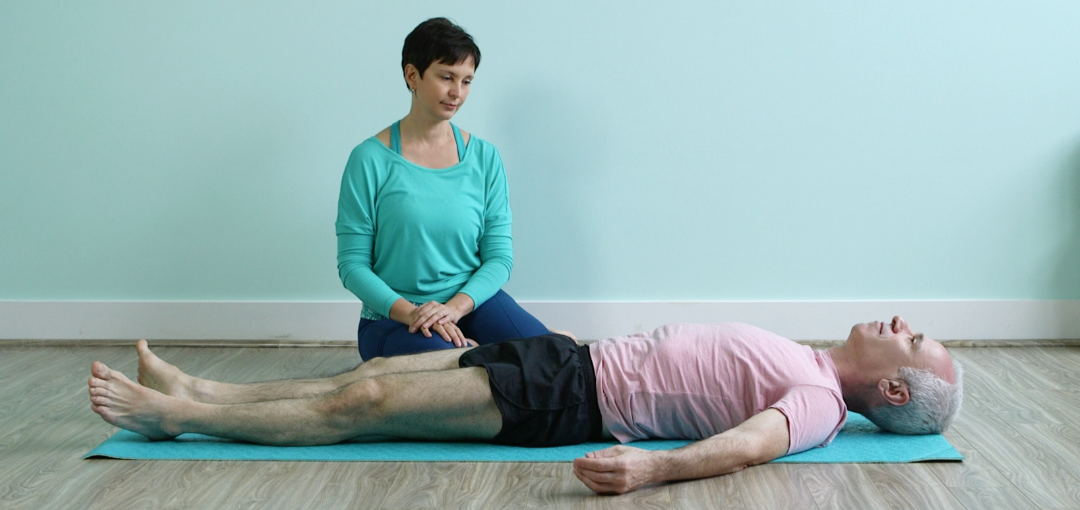

Many yoga teachers that I trained and tutored often ran into a problem of collecting too much information. They observe and record every little detail they encounter and then end up drowning in those details. This desire not to miss anything is completely understandable; we never know which detail ends up being the crucial one. Is it important that the student’s right foot is turned out farther then the left? Does it matter that she has an exaggerated lumbar curve? Is it relevant that she cannot feel the engagement in her hip flexors in Warrior pose? Details are important, yet the main question is whether or not they are relevant to the problem that the student is dealing with. How do we decide on what’s relevant? What if we miss something important?
There are different step-by-step templates for static and movement observations we can follow. Today I am inviting you to reframe your thinking and instead look for external clues that might help you get a glimpse into the student’s overall body story. We can think of those clues in terms of three categories: asymmetries, restrictions and discrepancies.
Asymmetries reflect the differences between the right and left, front and back and top and bottom. For example, if one of the student’s shoulders is higher than the other, we would record it as an asymmetry between the right and left shoulders. It can be an asymmetry in weight distribution (if the student’s body tends to lean forward in standing), or an asymmetry in muscular agonist/antagonist relationship (if the student’s quadriceps appear very tight, while the hamstrings are weak), and so on. Noting those asymmetries and bringing our student’s attention to them can give as valuable information on how they use their body and where they hold tension.
Restrictions reflect the areas that have limited range of motion, seem to be guarded or appear stiff and contracted. For example, if the student cannot raise her arms comfortably over her heard, it will indicate a restriction in her shoulders. Or if she can turn comfortably to her right, but not to her left, this will indicate both a restriction and an asymmetry. Restrictions can show up in how students hold their bodies, how they move, how they breathe and even in how they think, if they appear to be stuck in a particular way of interpreting their symptoms. Noticing those restrictions helps us identify where they appear to be stuck, which serves as a jump-off point for our investigation of where those restrictions are coming from.
Discrepancies reflect the difference between how the student experiences their body and what the teacher observes in real time. Discrepancies include not being able to tell where the body part is in space, which knee is pointing where, feeling like one side is heavier or denser than the other, and having gaps in sensations in specific body parts. Those types of discrepancies usually point out to the parts of the body where the student has either increased sensitivity or interrupted connection between the body part and the brain because of previous experiences. It is only possible to identify those discrepancies when the teacher encourages the student to continuously pay attention to specific body parts and maintains an open dialog about what the student feels and where. Identifying those discrepancies builds student’s interoception (awareness of inner sensations) and gives us insight into the parts that need our attention and care.
Once we identify the asymmetries, restrictions and discrepancies, it might be tempting to immediately attempt to even out the asymmetries, loosen up the restrictions and correct the discrepancies. A better approach would be to first let the body story unfold without trying to direct and control it. Afterwards, we can use movement, breath and awareness to bring blood flow, energy and attention to the asymmetrical, restricted and disconnected parts. Only after witnessing the challenges those body parts experience, validating their struggles, giving them undivided attention and listening to their stories can the healing process begin.
This process of attentive observation takes place in every yoga session and serves as a proverbial thread that leads us through the labyrinth of the student’s body story. It is essential to record those observations along with student’s comments right after the session so that important details don’t get lost. Next time we will talk about making the record-keeping process more interesting and engaging for the teacher–tune in!
[jetpack_subscription_form]
















Thanks Olga for your clear straight forward explanations. It’s a pleasure and a relief to count on your guidance and support ????
Although your affirmation “A better approach would be to first let the body story unfold without trying to direct and control it” definitely makes sense to me, I’m curious about what you exactly mean with that, the approach you use to apply this idea.
I’ll stay tunned in! ?
Thank you Ana! And you are right, we will be talking much more about “letting the body story unfold” in the coming months 🙂 I can’t wait to continue this conversation because it’s such powerful work. More to come… 🙂