What causes front knee pain and what can we do about it?
4“Get your earplugs ready” – jokes one of my students before attempting Chair pose. Over the years of working together we both got used to the loud crackling sound that her knees make when she squats. We muse about what it sounds like – an old barn door opening? – creaky stairs in the haunted house?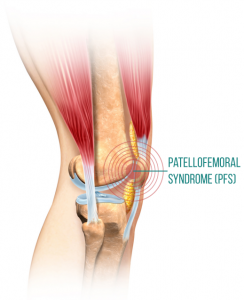
This characteristic grinding noise on movement is called “crepitus” and can potentially point to a condition called Patellofemoral syndrome (PFS). Symptoms of PFS include pain at the front of the knee, feeling stiffness in the knees after long immobility, difficulty walking down stairs, and this loud noise. Sometimes people report a feeling of “buckling” in the knees as if parts of the knee slip past each other instead of fitting closely together.
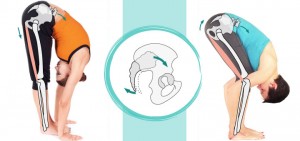
This feeling is not misleading. PFS is caused by femur (thigh bone) cartilage rubbing against patella (kneecap) cartilage when the knee is bent. “The range of motion for the patella is broader then most people understand. This bone moves superiorly [up] and inferiorly [down], but it can also move medially [in] and laterally [out], and it can rotate and tip in any direction. If pressure is not evenly distributed across the back of the patella, disruptions to the patella cartilage can occur. While this condition can be stopped or even reversed if it is caught early, long-term irritation can ultimately lead to permanent cartilage damage and osteoarthritis in the knee” (1).
Why does this happen? It usually happens because of overload or poor knee alignment.
1. Overload. Repetitive jumping motions along with other percussive activities can cause knee pain. But it can also be linked to being overweight, especially if the person leads sedentary lifestyle (which can result in weakening of the supporting musculature).
2. Poor alignment of the knee can happen for different reasons. Some of them include:
• Foot-related issues – flat feet, sprained ankles, poor footwear, running on uneven surfaces. They alter how the force of impact with the ground moves up the leg to the knee.
• Imbalanced muscle development between the hamstrings, quadriceps and IT band. PFS almost always involves a side pull on the kneecap.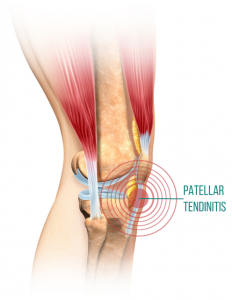
One worthy point to note is that PFS can be easily confused with patellar tendinitis (inflammation of the tendon that connects your knee cap to your shinbone) that also manifests as pain in front of the knee. “One clue that is sometimes useful is that patellar tendinitis often hurts going up stairs (resisted extension of the leg) while PFS may hurt going down stairs (weight of the femur pushing on the patella). However, these two conditions can certainly be present simultaneously.” (1) The strategies listed below could help with both conditions.
So what can we do about PFS? First, what we shouldn’t do – bouncing kind of exercise. The knee can get really irritated from running, aerobics or any other “high impact” exercise, so it is best to choose other activities, like walking, swimming, cycling or yoga (without any jumping).
In our yoga practice we can do the following:
1. Work on balanced development between the muscles that support the knee (quadriceps, hamstrings, TFL and hip rotators)
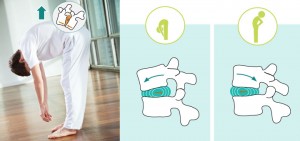
2. Pay very close attention to knee alignment in poses, especially when the knee is bearing weight. It is best to keep the knee over the ankle; avoid “droopy knee”.
3. Work on bearing weight on “four corners of the foot” in standing poses instead of collapsing your arches or leaning on the outer edge of the foot.
4. Strengthen the muscles of your feet and ankles.
5. Work on squatting positions in stages, over time, closely monitoring feet and knee alignment and your body’s feedback.
6. Avoid kneeling poses when the knee is irritated. Sometimes a student will be fine having both knees on the ground (as in Child’s pose, for example), but not comfortable putting weight on just one knee (as in a kneeling lunge, for example). We need to respect those limitations and offer different options.
The cracking sound that your knees make is not necessarily problematic by itself, but if it is accompanied by pain and/or swelling, it might point to underlying issues that need to be addressed. Next week we will talk about general yoga strategies for working with the knees. Tune in!
Resources
[jetpack_subscription_form]















I’m so incredibly grateful for your accessible, wise posts. Thank you ??
Thank you Chrissie!
Could you please suggest an alternative for the kneeling lunge. Thank you.
Hi Sandy! I usually just teach Warrior 1 as an alternative to a kneeling lunge. You can also try a regular Crescent lunge, but you will need to be more careful since it can be wobbly for the knee (hold on to something if necessary and keep an eye on the knee positioning).